For a professional streamer, an internet connection isn’t just a utility it is the lifeline of the business. A single dropped connection during a sponsored segment or a competitive tournament can cost revenue, reputation, and viewership.
While most streamers obsess over upload speeds and bitrates, few pay enough attention to Network Architecture. This guide breaks down the two most critical components of a secure streaming setup: the VPN (Virtual Private Network) and the VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network).
Think of your network like a castle:
The VPN is the moat and the camouflage that hides your castle from the outside world.
The VLAN is the internal system of locked doors that prevents a spy in the kitchen from getting into the treasury.
Part 1: The Outer Shield - VPNs
What is it?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) creates an encrypted tunnel between your computer and a server controlled by the VPN provider. Instead of your data traveling directly to a game server or website, it detours through this secure tunnel.
Why Streamers Need It
1. The Anti-DDoS Shield (Crucial)
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are the plague of the streaming world. Malicious actors flood your IP address with junk traffic, overwhelming your modem and knocking your stream offline.
Without a VPN: Your home IP address is visible to game servers and, in Peer-to-Peer (P2P) games (like GTA Online or older Call of Duty titles), to other players.
With a VPN: Attackers only see the IP address of the VPN server. If they DDoS that IP, the VPN server absorbs the hit. If the server goes down, you simply switch to a new VPN node, and your home internet remains untouched.
2. Doxxing and Swatting Prevention
“Swatting” relies on finding a streamer’s real-world location. While sophisticated attackers use social engineering, many start by resolving a streamer’s IP address to a physical location (Geolocation). A VPN masks your true location, making you appear as if you are in a different city or country.
3. Bypassing ISP Throttling
Streaming requires high, sustained upload bandwidth. Some Internet Service Providers (ISPs) identify this heavy traffic and intentionally slow it down (“throttling”). A VPN encrypts your traffic, preventing the ISP from seeing was you are doing, making it much harder for them to selectively throttle your stream.
The Trade-off: Ping & Performance
The biggest fear streamers have regarding VPNs is lag.
The Solution: Verwenden Sie die WireGuard protocol. It is significantly lighter and faster than older protocols like OpenVPN.
Split Tunneling: This feature allows you to route only specific apps through the VPN.
Scenario A (High Security): Route everything through the VPN. Essential for P2P games.
Scenario B (Performance): Route your browser and chat through the VPN (to hide IP from clicked links) but let the game run directly on your ISP connection for minimum ping. Warning: This leaves your IP exposed via the game client.
Part 2: The Inner Walls - VLANs
What is it?
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a method of slicing your single physical home network into multiple, isolated virtual networks. Even though all devices connect to the same router, they cannot “see” or talk to each other unless you explicitly allow it.
Why Streamers Need It
1. The “Smart Bulb” Threat
Your streaming PC is a fortress. But what about that $15 smart light strip behind you? Or the smart fridge in the kitchen? IoT (Internet of Things) devices are notoriously insecure and rarely updated. Hackers often compromise these weak devices to gain a foothold in your network. Once inside the “Smart Bulb,” they can move laterally to your PC, steal session tokens, and hijack your Twitch/YouTube account.
With a VLAN: You put the smart bulb on a separate “IoT VLAN.” If it gets hacked, the attacker is trapped in that VLAN and cannot access your Streaming PC.
2. Network Congestion & QOS
Imagine your roommate starts downloading a 100GB game file while you are live. On a standard flat network, packets collide, and your stream drops frames.
With a VLAN: You can segment traffic and apply Quality of Service (QoS) rules. You can tell your router: “VLAN 10 (Streaming) always gets priority over VLAN 30 (Guest Network).”
Part 3: The Synergy (How they work together)

To be truly secure, you need both. A VPN stops the enemy at the gate; the VLAN limits the damage if they somehow sneak in.
The “Ironclad” Network Topology
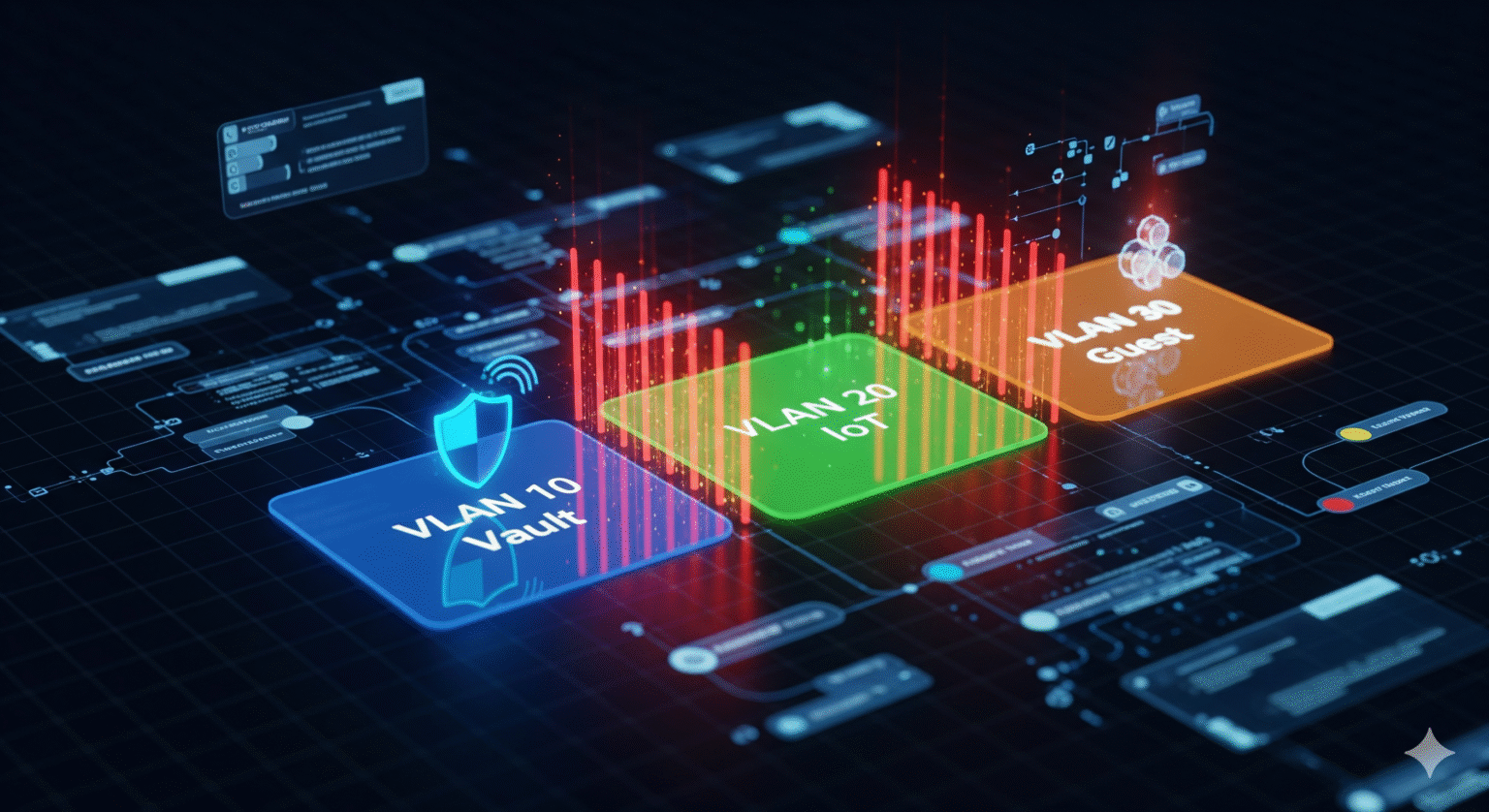
Here is the recommended setup for a professional content creator:
VLAN 10: The “Vault” (High Priority)
Devices: Streaming PC, Gaming Console, Stream Deck, Audio Interface.
Rules: Strict firewall. Can access the internet, but cannot be accessed from the internet.
VPN Strategy: This device runs the VPN client (or the router routes this VLAN through a VPN tunnel).
VLAN 20: The “IoT Jungle” (Low Trust)
Devices: Smart lights, smart thermostats, cheap IP cameras, smart fridges.
Rules: Client Isolation enabled (devices can’t even talk to each other). No access to VLAN 10. Internet access only for cloud control.
VLAN 30: The “Guest/General” Zone
Devices: Roommates’ phones, visiting friends, the TV in the living room.
Rules: Standard internet access. Bandwidth limits applied so they don’t eat your upload speed. No access to VLAN 10.
Part 4: Implementation Checklist

To pull this off, you need more than the standard ISP-provided modem.
Hardware Upgrade:
Router: You need a router that supports VLAN tagging (802.1Q) and decent VPN processing power.
Prosumer: Ubiquiti Dream Machine, Firewalla Gold, or a Netgate (pfSense) box.
Budget/DIY: A high-end ASUS router running Asuswrt-Merlin firmware.
Switch: A “Managed Switch.” Unmanaged switches strip VLAN tags and ruin the segmentation.
Configuration Steps:
Schritt 1: Create your VLANs (IDs 10, 20, 30) in the router interface.
Schritt 2: Assign Wi-Fi SSIDs to VLANs (e.g., “Stream_Net” -> VLAN 10, “Smart_Home” -> VLAN 20).
Schritt 3: Set Firewall Rules. The most important rule is “Block access from VLAN 20 to VLAN 10.”
Schritt 4: Install the VPN on the Streaming PC (for granular control) OR at the router level (to protect the whole VLAN 10).
Testing:
Connect your phone to the IoT network. Try to ping your Streaming PC. If the ping fails, your walls are solid.
